

1Ĭanale and Kelly reported 23 patients undergoing conservative therapy with prolonged non- weight bearing (for >9 months) or PTB. The role becomes controversial in patients with sclerotic zones and late presentation of the disease, since the exact role of non- weight bearing in the prevention of talar collapse has never been proven. Non- weight bearing is particularly beneficial in early cases or those with evidence of subchondral atrophy or revascularization when the talus is structurally weak. X-ray ankle joint lateral view of 20 year long term followup showing that Blair's Fusion done by excision of talar body and anterior tibial sliding Graft after which the patient recovered and currently is working as a Restaurant manager in Australia Nonoperative management (non weight bearing, protected weight bearing using splints such as the patellar tendon brace, and extracorporeal shock wave therapy ) 7 (b) Surgical joint-sparing procedures (core decompression, bone grafting – vascularized or non vascularized autografts) 9, 10 3] (c) Joint sacrificing procedures (partial or total talar replacement ) 18, 19 (d) Salvage procedures (talectomy, arthrodesis of ankle, subtalar, tibionavicular, tibiocalcaneal, or tibiotalocalcaneal joints) 21, 22 (e) Total ankle replacement (TAR) 31, 32. The various treatment modalities described in literature for treating AVN talus include the following: The preoperative workup and imaging gives an idea about the aetiology, duration, rate of progression, extent of the AVN, including the stage of the disease, and the degree of disability of the patient. 5, 6 The treatment of AVN talus can also be frustrating and is a major challenge to the surgeon the results after talus collapse are suboptimal in many cases, even in the best of surgical hands. 4 The diagnosis of AVN talus can be a challenge, and the surgeon needs to anticipate it, especially in traumatic cases with significantly displaced body fragment. 1, 2, 3 Apart from posttraumatic causes, it can occasionally have non-traumatic aetiologies ranging from alcoholism, steroid use, dyslipidemia, or an idiopathic cause. Future prospective, randomized studies are necessary to guide the conservative and surgical management of talar AVN.Īvascular necrosis (AVN) of the talus is a dreaded sequel to talar fractures, with the chances of AVN increasing with the severity of trauma and the associated damage to the already precarious blood supply. Role of vascularized bone grafting is still not defined clearly and needs further investigation. Arthrodesis should be saved as a salvage procedure in late cases with arthritis and collapse, and a tibiotalocalcaneal fusion with bone grafting may be needed in cases of significant bone loss. If that fails, core decompression can be considered.
Early talar AVN seems best treated with protected weight bearing and possibly in combination with extracorporeal shock wave therapy. Based on the analysis of available literature, we make certain recommendations for managing patients of AVN talus depending on identified disease factors such as early or late presentation, extent of bone involvement, bone collapse, and presence or absence of arthritis. We looked to identify the study quality, imprecise and sparse data, reporting bias, and the quality of evidence. The interventions of interest included hindfoot fusion, conservative measures, bone grafting, vascularized bone graft, core decompression, and talar replacement. Forty-one studies met the inclusion criteria of the 335 abstracts screened. The articles' abstracts were read by two of the authors. We searched MEDLINE and PUBMED using keywords and MESH terminology. We have done a systematic review of the literature with the following aims: (1) identify and summarize the available evidence in literature for the treatment of talar AVN, (2) define the usefulness of radiological Hawkins sign and magnetic resonance imaging in early diagnosis, and (3) provide patient management guidelines. The most common cause is a fracture of the talus.
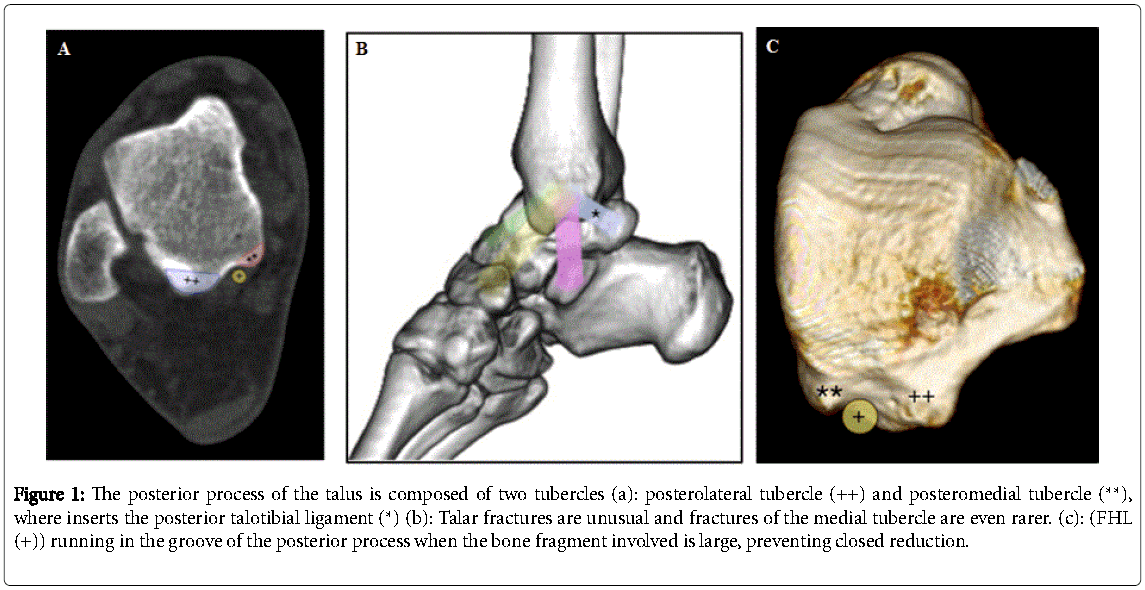
Avascular necrosis (AVN) of the talus can be a cause of significant disability and is a difficult problem to treat.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
